PIPELINE
Breaking new ground from concept to clinic
PIPELINE
Breaking new ground from concept to clinic
- Discovery
- IND Enabling
- Phase 1A
- Phase 1B/2
- Pivotal
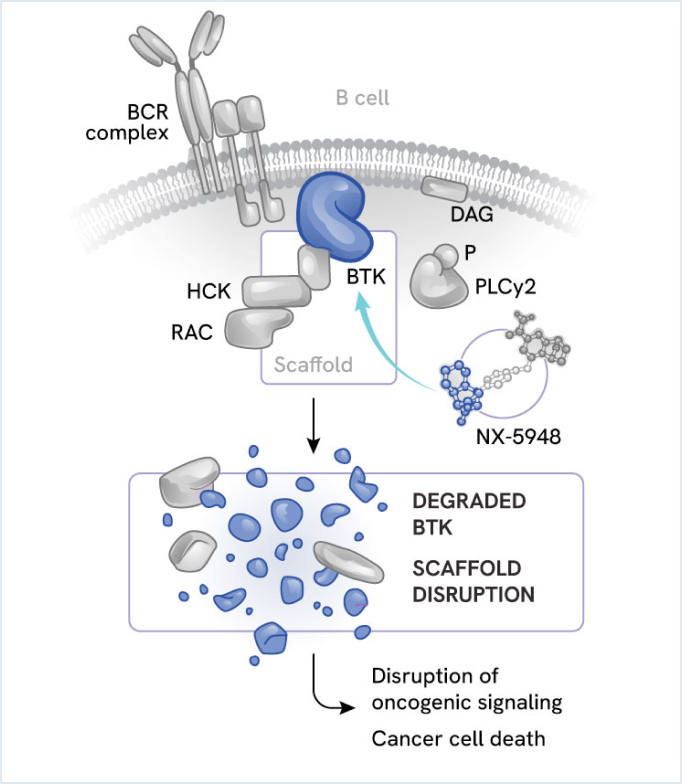
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948): Oral, CNS-penetrant BTK degrader
Bexobrutideg is an oral, CNS-penetrant, small molecule degrader of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) being evaluated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM).
Scientific rationale
BTK is a master regulator of B-cell activity and is a clinically validated target for hematologic malignancies. While BTK inhibitors have shown clinical success, drug resistance often emerges due to acquired mutations in BTK.
By removing BTK rather than merely inhibiting its activity, bexobrutideg may circumvent both kinase domain mutations and scaffolding-mediated resistance mutations to provide more durable responses. Additionally, its brain penetration suggests potential for treating challenging CNS-involved leukemias and lymphomas.
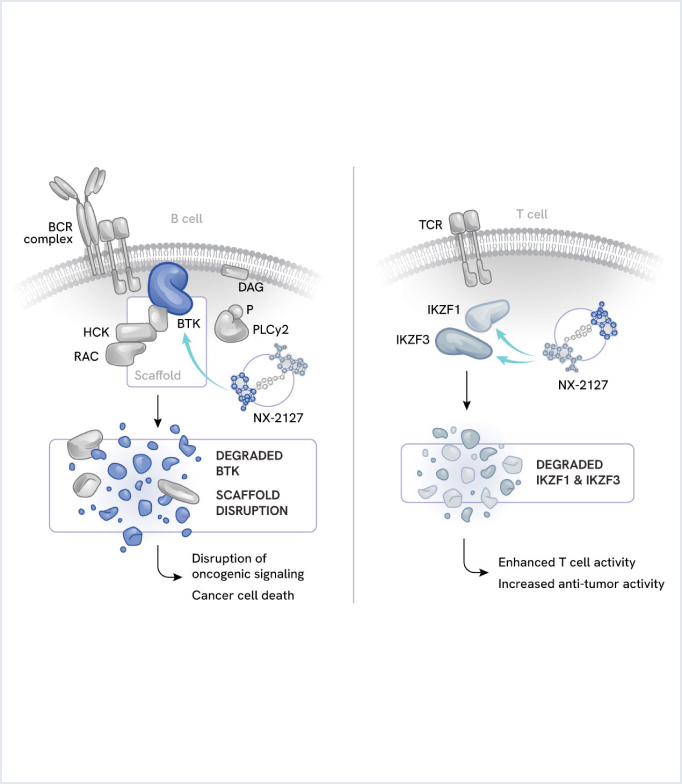
Zelebrudomide (NX-2127): Oral dual degrader of BTK and cereblon neosubstrates
Zelebrudomide is an oral small molecule dual degrader targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) and the cereblon neosubstrates IKZF1 (Ikaros) and IKZF3 (Ailos), which are implicated in B and T cell activity. Zelebrudomide is being evaluated in patients with B-cell malignancies with a focus on aggressive forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Scientific rationale
B-cell malignancies often rely on multiple signaling pathways for growth and survival. Two key pathways include:
- BTK: A master regulator of B-cell activity. Aberrant BTK signaling can drive malignant B-cell proliferation.
- IKZF1/3: These transcription factors play crucial roles in B-cell development and function.
Importantly, IKZF1/3 also represses proinflammatory cytokine expression from T cells. This dual role of IKZF1/3 in malignant B cells and T cells provides a unique opportunity for therapeutic intervention. By combining BTK degradation with cereblon-mediated immunomodulatory activity, zelebrudomide aims to provide enhanced therapeutic benefit across a spectrum of B-cell malignancies.
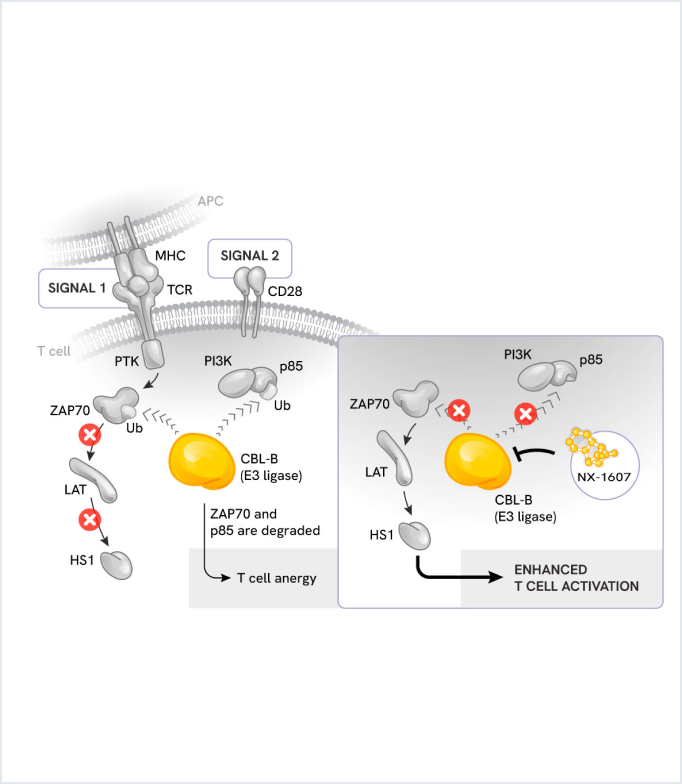
NX-1607: Novel CBL-B inhibitor for immuno-oncology
NX-1607 is a first-in-class, small molecule inhibitor of Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene-b (CBL-B), an E3 ligase that acts as a critical checkpoint in the immune system. This innovative compound is being developed as part of Nurix’s immuno-oncology program and is currently being evaluated in advanced malignancies.
Scientific rationale
CBL-B plays a crucial role in regulating immune cell function:
- In the context of cancer, CBL-B acts as a brake on the immune system by negatively regulating T cell activation, inhibiting NK cell activity, and suppressing overall immune responses.
- CBL-B achieves this immunosuppressive effect through the degradation of specific inhibitory signaling proteins downstream of the T cell receptor.
- CBL-B operates in immune cells and the tumor microenvironment, making it a compelling immuno-oncology target.
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948)
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948): Oral, CNS-penetrant BTK degrader
Bexobrutideg is an oral, CNS-penetrant, small molecule degrader of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) being evaluated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM).
Scientific rationale
BTK is a master regulator of B-cell activity and is a clinically validated target for hematologic malignancies. While BTK inhibitors have shown clinical success, drug resistance often emerges due to acquired mutations in BTK.
By removing BTK rather than merely inhibiting its activity, bexobrutideg may circumvent both kinase domain mutations and scaffolding-mediated resistance mutations to provide more durable responses. Additionally, its brain penetration suggests potential for treating challenging CNS-involved leukemias and lymphomas.
Zelebrudomide (NX-2127)
Zelebrudomide (NX-2127): Oral dual degrader of BTK and cereblon neosubstrates
Zelebrudomide is an oral small molecule dual degrader targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) and the cereblon neosubstrates IKZF1 (Ikaros) and IKZF3 (Ailos), which are implicated in B and T cell activity. Zelebrudomide is being evaluated in patients with B-cell malignancies with a focus on aggressive forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Scientific rationale
B-cell malignancies often rely on multiple signaling pathways for growth and survival. Two key pathways include:
- BTK: A master regulator of B-cell activity. Aberrant BTK signaling can drive malignant B-cell proliferation.
- IKZF1/3: These transcription factors play crucial roles in B-cell development and function.
Importantly, IKZF1/3 also represses proinflammatory cytokine expression from T cells. This dual role of IKZF1/3 in malignant B cells and T cells provides a unique opportunity for therapeutic intervention. By combining BTK degradation with cereblon-mediated immunomodulatory activity, zelebrudomide aims to provide enhanced therapeutic benefit across a spectrum of B-cell malignancies.
NX-1607
NX-1607: Novel CBL-B inhibitor for immuno-oncology
NX-1607 is a first-in-class, small molecule inhibitor of Casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene-b (CBL-B), an E3 ligase that acts as a critical checkpoint in the immune system. This innovative compound is being developed as part of Nurix’s immuno-oncology program and is currently being evaluated in advanced malignancies.
Scientific rationale
CBL-B plays a crucial role in regulating immune cell function:
- In the context of cancer, CBL-B acts as a brake on the immune system by negatively regulating T cell activation, inhibiting NK cell activity, and suppressing overall immune responses.
- CBL-B achieves this immunosuppressive effect through the degradation of specific inhibitory signaling proteins downstream of the T cell receptor.
- CBL-B operates in immune cells and the tumor microenvironment, making it a compelling immuno-oncology target.
BRAF degrader
Multiple
Multiple
Undisclosed
Multiple
- Discovery
- IND Enabling
- Phase 1A
- Phase 1B/2
- Pivotal
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948): BTK degrader for autoimmune disorders
Bexobrutideg is an oral, CNS-penetrant, small molecule degrader of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) being developed to address autoimmune disease.
Scientific rationale
BTK acts as a nexus for allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory processes. It transduces signals downstream of the B-cell receptor, toll-like receptor, and Fc receptors in B cells and myeloid cells. BTK regulates B-cell and myeloid cell responses, mediating auto-antibody and inflammatory cytokine production, mast cell degranulation, and tissue damage.
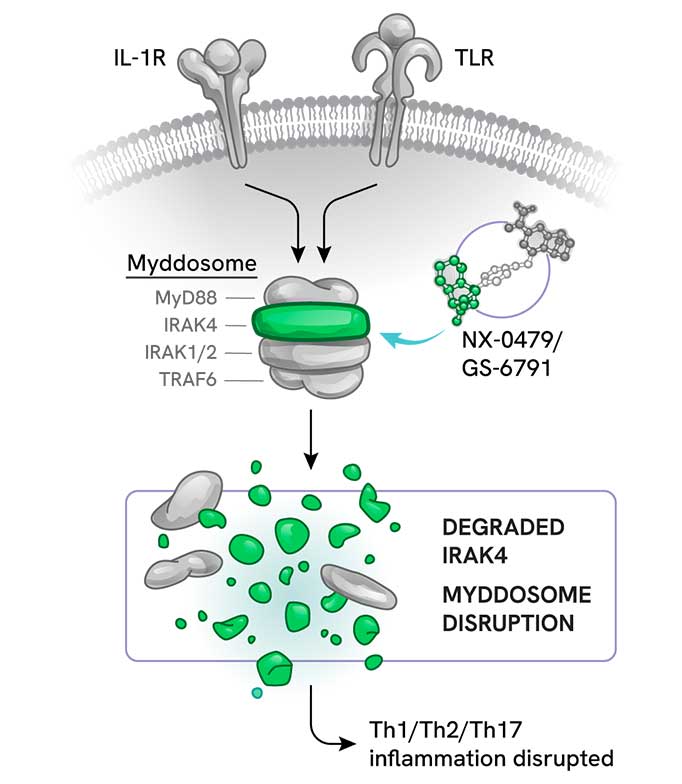
NX-0479: Novel IRAK4 degrader for chronic inflammatory diseases
NX-0479 is an innovative small molecule degrader targeting Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4). This compound is being developed to address chronic inflammatory diseases, with a particular focus on rheumatoid arthritis.
Scientific rationale
IRAK4, a master regulator of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) and Interleukin-1 Receptor (IL-1R) signaling pathways, plays a crucial role in inflammatory processes. Inappropriate activation of these receptors promotes inflammation and autoimmunity through the release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Because IRAK4 exhibits both kinase and scaffolding functions, degradation of IRAK4 aims to achieve more complete blockade of the TLR/IL-14 signaling pathways and yield broader anti-inflammatory effects than inhibition alone.
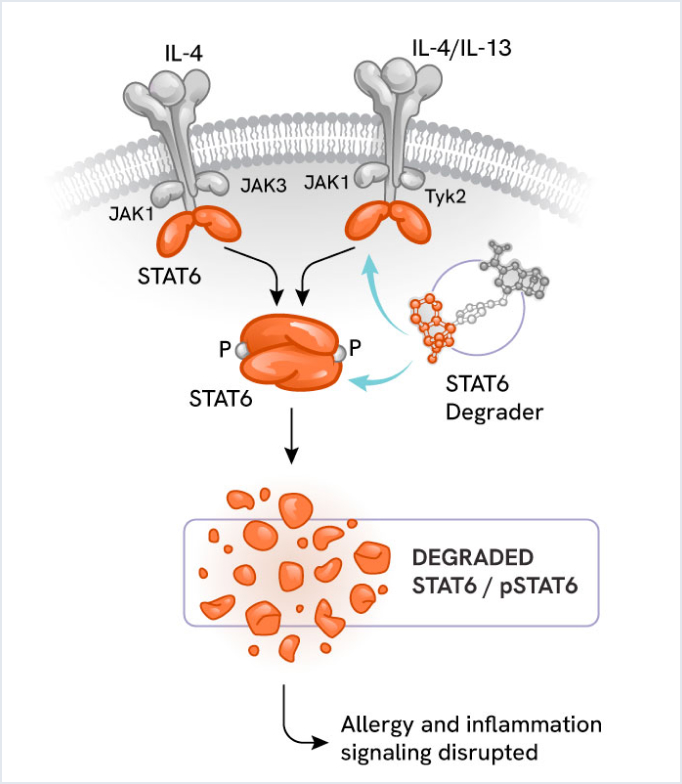
STAT6 degrader: Novel approach for allergic and inflammatory disorders
Nurix’s STAT6 degrader is an innovative compound designed to address allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory processes.
Scientific rationale
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6, or STAT6, is a key transcription factor in the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. It acts downstream of the inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, driving Th2-mediated inflammatory disorders (e.g., allergies, asthma, eczema). By degrading STAT6, this compound aims to reduce Th2-mediated inflammation more effectively than traditional inhibitors.
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948)
Bexobrutideg (NX-5948): BTK degrader for autoimmune disorders
Bexobrutideg is an oral, CNS-penetrant, small molecule degrader of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) being developed to address autoimmune disease.
Scientific rationale
BTK acts as a nexus for allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory processes. It transduces signals downstream of the B-cell receptor, toll-like receptor, and Fc receptors in B cells and myeloid cells. BTK regulates B-cell and myeloid cell responses, mediating auto-antibody and inflammatory cytokine production, mast cell degranulation, and tissue damage.
NX‑0479/GS‑6791
NX-0479: Novel IRAK4 degrader for chronic inflammatory diseases
NX-0479 is an innovative small molecule degrader targeting Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4). This compound is being developed to address chronic inflammatory diseases, with a particular focus on rheumatoid arthritis.
Scientific rationale
IRAK4, a master regulator of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) and Interleukin-1 Receptor (IL-1R) signaling pathways, plays a crucial role in inflammatory processes. Inappropriate activation of these receptors promotes inflammation and autoimmunity through the release of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Because IRAK4 exhibits both kinase and scaffolding functions, degradation of IRAK4 aims to achieve more complete blockade of the TLR/IL-14 signaling pathways and yield broader anti-inflammatory effects than inhibition alone.
NX-3911
STAT6 degrader: Novel approach for allergic and inflammatory disorders
Nurix’s STAT6 degrader is an innovative compound designed to address allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory processes.
Scientific rationale
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6, or STAT6, is a key transcription factor in the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. It acts downstream of the inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, driving Th2-mediated inflammatory disorders (e.g., allergies, asthma, eczema). By degrading STAT6, this compound aims to reduce Th2-mediated inflammation more effectively than traditional inhibitors.